The Americas
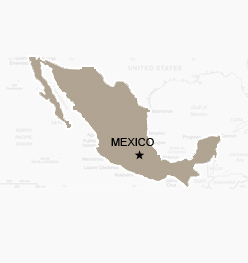
Mexico
Capital Mexico City
Population 111.2 million
Life Expectancy 76.06
Access to clean water 95%
Adult literacy 91%
Under five mortality 18.42 per 1,000 live births
GDP per head (US$ PPP) $14,200
-
Country Fact Sheet
 This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programmes in Mexico.
This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programmes in Mexico.
Mexico Joint Programmes Fact Sheet.pdf (171 KB)
Our Joint Programmes
Establishing effective and democratic water and sanitation (W&S) management in Mexico to support the achievement of the MDGs Although the states of Chiapas, Tabasco and Veracruz account for most of Mexico's water resources, water and sanitation service coverage is very uneven due to socioeconomic factors, ethnicity and gender inequality. The aim of this Joint Programme was to improve the integrated management of water in peri-urban and rural areas of Mexico and to combat poverty from the standpoint of environmental sustainability and gender equality. The programme contributed to achieving MDGs 1, 3 and 7 by diminishing inequalities in accessing an essential resource, particularly for women and the poor. Conflict prevention, development of agreements and peace building for internally displaced persons (IDPs) in Chiapas State The 1994 clash between the Mexican State and the Zapatista resulted in tens of thousands of people being driven off their land. Many of these remain displaced, fueling strife and perpetuating poverty in Mexico's least developed state. The aim of this Joint Programme was to reduce conflict and tension in 25 communities in Chiapas by strengthening the criminal justice system, improving security and developing a culture of peace.IN THE NEWS
STORIES
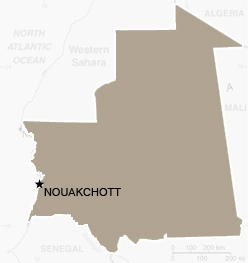
Mauritania
Capital Nouakchott
Population 3.1 million
Life Expectancy 60.37
Access to clean water 60%
Adult literacy 51.2%
Under five mortality 63.42 per 1,000 live births
GDP per head (US$ PPP) $2,100
 This evaluation is a knowledge-generating exercise whose goal is to: 1) Assess the MDG-F's contribution, at national level, to the achievement of the MDGs, the principles of the Paris Declaration and the UN reform initiative to “Deliver as One”; 2) Identify best practices and lessons learned in order to inform future joint programming for development; and 3) Connect local level programme interventions with national level policy-making processes by highlighting successful pilot initiatives with the potential for replication and scale-up.
This evaluation is a knowledge-generating exercise whose goal is to: 1) Assess the MDG-F's contribution, at national level, to the achievement of the MDGs, the principles of the Paris Declaration and the UN reform initiative to “Deliver as One”; 2) Identify best practices and lessons learned in order to inform future joint programming for development; and 3) Connect local level programme interventions with national level policy-making processes by highlighting successful pilot initiatives with the potential for replication and scale-up.
Mauritania_Country Final evaluation.pdf (1.97 MB)-
Country Fact Sheet
 This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programmes in Mauritania.
This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programmes in Mauritania.
Mauritania Joint Programmes Fact Sheet.pdf (200 KB)
MDG-F Case Study Evaluation
Our Joint Programmes
Scaling up the fight against child hunger and malnutrition in southeast Mauritania This Joint Programme was established to combat an alarming increase in malnutrition in two southeastern regions of Mauritania, where the underweight prevalence in children under 5 rose from 35% in 2007 to 40% in 2008, more than twice the national average. The programme comprised a package of integrated interventions for the prevention and treatment of malnutrition, targeting more than 420,000 women and children with actions to improve food security, change feeding behaviors and strengthen the management of malnutrition. Mainstreaming Local Environmental Management in the Planning Process Southwestern Mauritania faces considerable environmental problems, with deteriorating natural resources and populations living in conditions of poverty, precarious health and a lack of basic services. In rural areas, only 20% of households have access to sanitation and nearly two thirds of people live below the poverty line, further exacerbating resource degradation. The aim of this Joint Programme was to promote sustainable management of natural resources and access to water and sanitation, and to ensure that environmental issues are taken into account in national planning processes. Strengthening conflict prevention capacities and the rule of law in Mauritania An explosion of ethnic tensions in 1989 precipitated a mass expulsion of tens of thousands of Mauritanians and produced a climate of tension, uncertainty and animosity. Declining living conditions, rising unemployment and poverty, and the uneven distribution of resources exacerbated traditional sources of conflict -- access to land and water -- and social prejudices and discrimination became rampant. The Joint Programme's goal was to reduce conflict and inter-community tensions by promoting national unity and the rule of law, improving the equal distribution of resources and creating conflict resolution mechanisms. Heritage, tradition and creativity for sustainable development in Mauritania Part of Mauritania's strategic fight against its high poverty rates is to develop tourism and related areas. The Joint Programme supported this goal by encouraging the growth of Mauritania's cultural sector as a way to drive development and generate incomes, with particular emphasis on women's activities. The programme focused on strengthening the national capacity to develop and promote cultural businesses, as well as the management, conservation and enhancement of the country's cultural heritage.IN THE NEWS
STORIES
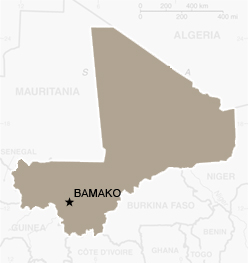
Mali
Capital Bamako
Population 12.6 million
Life Expectancy 50:35
Access to clean water 60%
Adult literacy 46.4%
Under five mortality 102.05 per 1,000 live births
GDP per head (US$ PPP) $1,200
-
Country Fact Sheet
 This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programme in Mali.
This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programme in Mali.
Mali Joint Programme Fact Sheet.pdf (139 KB)
Our Joint Programmes
Improving Child Nutrition and Food Security in the most vulnerable municipalities in Mali Mali has one of the highest rates of child malnutrition and food insecurity in the world. One in six children suffers from acute malnourishment and more than a third are stunted from a lack of proper nutrients. Though Mali has made progress in reducing child deaths, more than half of those that occur are due to malnutrition. The aim of the Joint Programme was to improve food security and the nutritional status of women and children, enhance Mali's ability to monitor food and nutrition issues and ensure that these are considered in national and community policy-making.STORIES
Eastern Europe
The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
Capital Skopje
Population 2 million
Life Expectancy 74.68
Access to clean water n/a
Adult literacy 96.1%
Under five mortality 9.01 per 1,000 live births
GDP per head (US$ PPP) $9,100
-
Country Fact Sheet
 This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programmes in the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.
This Fact Sheet summarizes the key achievements of the Joint Programmes in the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia.
FYR Macedonia Joint Programme Fact Sheet.pdf (116 KB)